Syllabus of Zoology(hons.) CBCS
INVERTEBRATE ZOOLOGY B.Sc 1st Semester
CORE COURSE I SYLLABUS
PAPER
NAME- ANIMAL DIVERSITY
“Protist
to Pseudo Coelomates”
Theory-
Unit 1- Protesta,Parazoa,Metazoa
General
Character and classification upto classes (phylum- protozoa)
Study of :
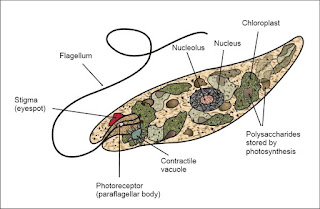
1.Euglena 2.Amoeba 3.Paramecium
- Life cycle
and Pathogenisity of Plasmodium Vivax and Entamoeba Histolytica
- Locomotion
and Reproduction in Protista
- Evolution of
symmetry and segmentation of metazoa
Unit 2-Porifera
-General
characteristics and classification upto classes
-Canal system
and spicules in Sponges
Unit 3- Cnidaria
-General
characteristics and Classification upto classes
-Metagenesis
in Obelia
-Polymorphism
in cnidaria, corals and coral reef
Unit 4- Ctenophora
-General
characteristics and Evolutionary Significance
Unit 5- Platyhelmenthes
-General
characteristics and classification upto classes
-Life cycle
and pathogenisity of Fasciola hepatica
and Taenia solium
Unit 6- Nemathhelmenthes
-General
characteristics and classification upto classes
-Life cycle
and pathogenisity of Ascaris lumbricoides and Wuchereria bancrofti
-Parasitic
adaptation in helminthes.
Practicals-
1.
Study of whole mount of Euglena,Amoeba,Paramecium, Binary fission and
conjugation in paramecium
2.
Examination of pond water collected from different places for diversity in
protest
3.
Study of Sycon(T.S and L.S), Hyalonema, Euplectella, Spongilla
4.
Study of Obelia, Physallia, Millepora, Aurellia , Tubipora, Corallium,
Alcyonium, Gorgonia, Metridium, Pennatula, Fungia,Meandrina, Madrepora
5.
One specimen/slide of any Ctenophora
6.
Study of Adult Fasciola hepatica,Taenia solium and their life cycles
7.
Study of adult Ascaris Lumbricoides and its life stages.
B.Sc 1st Semester
CORE COURSE II SYLLABUS
PAPER NAME- ECOLOGY
“Principles of Ecology”
THEORY
Unit 1:Introduction to Ecology
History of ecology, Autecology and synecology, Levels of organization,
Laws of limiting factors, Study of physical factors
Unit2:Population
-Unitary and Modular populations
-Unique and group attributes of population: Density, natality, mortality,
life tables, fecundity tables, survivorship curves, age ratio, sex ratio,
dispersal and dispersion Exponential and logistic growth, equation and
patterns, r and K strategies Population regulation - density-dependent
and independent factors
-Population interactions, Gause’s Principle with laboratory and field
examples, Lotka-Volterra equation for competition and Predation,
functional and numerical responses
Unit3:Community
-Community characteristics: species richness, dominance, diversity,
abundance, vertical stratification, Ecotone and edge effect; Ecological
succession with one example
-Theories pertaining to climax community
Unit4:Ecosystem
-Types of ecosystems with one example in detail, Food chain: Detritus
and grazing food chains, Linear and Y-shaped food chains, Food web,
-Energy flow through the ecosystem, Ecological pyramids and Ecological
efficiencies
-Nutrient and biogeochemical cycle with one example of
Nitrogen cycle Human modified ecosystem
Unit 5:Applied Ecology 4
-Ecology in Wildlife Conservation and Management
PRACTICALS-
1. Study of life tables and plotting of survivorship curves of different
types from the hypothetical/real data provided
2. Determination of population density in a natural/hypothetical community by quadrate methodandcalculationofShannon-Weinerdiversityindexforthesamecommunity
3. Study of an aquatic ecosystem: Phytoplankton and zooplankton,
Measurement of area, temperature, turbidity/penetration of light, determination of
pH, and Dissolved Oxygen content(Winkler’smethod).
4. Report on a visit to National Park/Biodiversity Park/Wild life sanctuary


Comments
Post a Comment